What Defines an Accounting System?
An accounting system is a structured set of processes and tools used to record, classify, summarize, analyze, and report financial transactions. It tracks income, expenses, assets, and liabilities, producing key financial statements like balance sheets and income statements. Accounting systems can be manual, computerized, or cloud-based, and may use single-entry or double-entry bookkeeping. They provide accurate financial data to support decision-making, ensure compliance, and improve business efficiency.
How is an Accounting System structured to manage financial data?
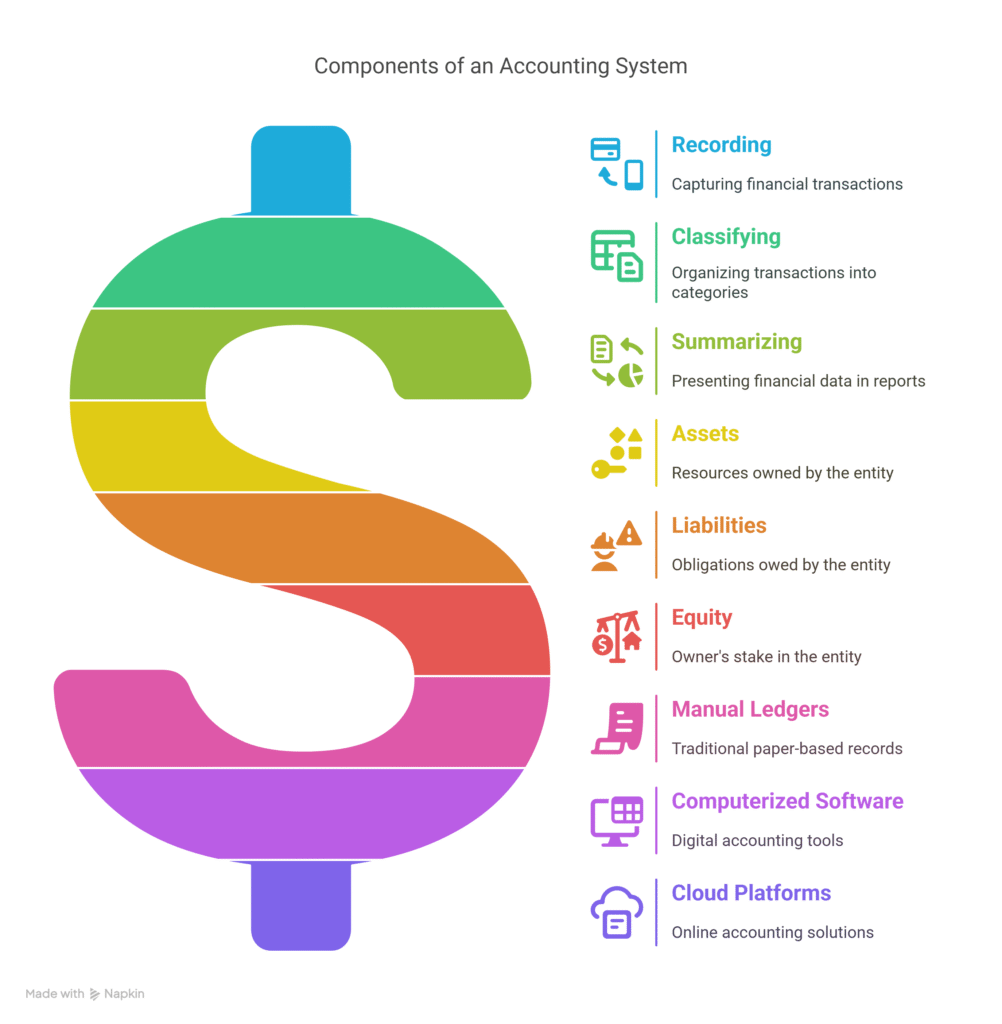
An accounting system is a structured framework for managing financial data, including recording, classifying, and summarizing transactions. It handles key elements like assets, liabilities, and equity, with examples such as manual ledgers, computerized software, and cloud platforms. Accounting systems improve accuracy and decision-making. The global accounting software market is projected to reach $20 million by 2026. Accountants use these systems to record and report finances, a practice dating to Luca Pacioli’s 15th-century double-entry bookkeeping. Types include single-entry, double-entry, manual, computerized, and cloud-based systems.
What purpose does an Accounting System serve in an organization?
An accounting system is a structured method or software that manages a business’s financial activities, including tracking income, expenses, invoices, and liabilities. Its key functions include recording transactions, classifying and summarizing financial data, analyzing reports, and reporting to stakeholders. The primary purpose is to provide accurate, real-time financial information that enables business owners and stakeholders to make informed decisions, ensure compliance with regulations, and effectively manage cash flow.
| Purpose | Description |
| Decision-Making | Supplies reliable data for operational and strategic choices |
| Compliance | Ensures adherence to tax and regulatory standards |
| Financial Management | Helps monitor cash flow, expenses, and income |
| Error Reduction | Automates calculations to minimize mistakes |
| Collaboration | Facilitates access and sharing of financial data remotely |
Accounting systems support internal users like managers and employees for budgeting and performance analysis, and external users such as investors and auditors for assessing company health. Evolving from manual ledgers to computerized and cloud-based platforms, these systems streamline financial management and improve business efficiency.
Why Are Accounting Systems Indispensable for Businesses?
Accounting systems are crucial because they manage and automate financial activities—from documenting transactions and syncing data across banking and credit accounts to generating real-time reports on profit, loss, and cash flow. They reduce manual errors, save time, and ensure tax compliance by tracking documents and preparing tax forms efficiently. Scalable and integrated with payroll, inventory, and CRM systems, these systems support business growth and streamline operations. Cloud-based solutions offer remote access, enhanced security, and automatic updates. By improving financial visibility, collaboration, and control, accounting systems empower businesses to avoid cash flow gaps, attract investors, and make informed decisions, ensuring sustainable growth and regulatory compliance.
How do Accounting Systems enhance financial accuracy and efficiency?
Accounting systems enhance financial accuracy and efficiency by processing transactions in real time, ensuring data is always current and consistent. Automation minimizes manual errors through tasks like data entry, invoice processing, bank reconciliation, and report generation. Integration with ERP, CRM, payroll, and inventory systems unifies financial data, reducing discrepancies. Advanced AI and machine learning tools detect anomalies and predict trends, improving accuracy. Automated reconciliation speeds up month-end closing and error detection. Cloud-based systems offer secure, remote access with automatic updates, boosting flexibility. These systems streamline reporting with customizable dashboards, support compliance and audit readiness, and free finance teams to focus on strategic tasks, ultimately enabling better decision-making and business growth.
In what ways do Accounting Systems support strategic decision-making?
Accounting systems play a pivotal role in supporting strategic decision-making by providing essential financial information that informs business owners. Utilizing accounting software, these systems generate comprehensive financial statements such as the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows, which collectively depict a firm’s financial position. Through double-entry accounting and adherence to generally accepted accounting principles, accountants ensure accurate recording transactions involving assets and liabilities, equity, and liabilities.
Furthermore, the application of managerial accounting and cost accounting enables business owners to analyze financial data effectively, guiding them in making informed decisions regarding accounts receivable and cash flow. By employing various accounting methods, such as accrual accounting or the cash method of accounting, organizations can optimize their bookkeeping practices, ensuring compliance with international financial reporting standards and maintaining integrity in their accounting records.
Ultimately, the integration of an efficient accounting information system not only streamlines the recording of transactions but also enhances the accuracy of financial accounting. This, in turn, empowers accountants to prepare detailed financial statements that reflect the true financial position of the organization at the end of an accounting period, ensuring that stakeholders can rely on the information presented for strategic planning and decision-making
How do Accounting Systems ensure regulatory compliance and control?
In the introduction to accounting, it is essential to understand how accounting systems facilitate regulatory compliance and control over a company’s financial activities. By employing a double-entry accounting system, organizations can accurately record financial transactions through debits and credits, ensuring that each entry reflects a corresponding change in the side of the accounting equation, which comprises assets, liabilities, and equity. This adherence to established accounting standards fosters transparency and reliability in financial records.
Furthermore, accounting software will allow companies to generate essential documents such as invoices and statements of financial position, which provide insights into the company’s financial health. By applying accounting basics and accounting concepts, businesses can track common stock, notes payable, and profit and loss statements, thus enhancing their ability to manage liability and equity effectively. The benefits of accounting extend beyond compliance, as they also promote informed decision-making regarding the provision of goods or services.
What Key Components Do Most Accounting Systems Include?
Most accounting systems encompass several important accounting components essential for effective financial management. A fundamental element is the double-entry system, which ensures accuracy by recording every transaction in two accounts, thereby supporting double entry accounting. In contrast, single-entry accounting may be utilized for simpler operations, although it lacks the robustness of double-entry methods. These systems are designed to provide accurate financial information, which is crucial for an organization’s financial health.
Furthermore, using an accounting system involves understanding the basics of accounting and familiarizing oneself with various accounting terms. Accounting professionals rely on accounting entries made throughout the accounting year to fulfill various accounting purposes. While some organizations may still employ manual systems, the efficiency of automated systems significantly enhances the accuracy of accounting tasks and streamlines financial management.
Ultimately, the choice of accounting methods—whether simple accounting or more complex frameworks—should align with the organization’s needs to ensure that similar information is accessible for critical business decisions. Thus, using accounting is not merely a procedural necessity but a strategic approach to sustaining an organization’s financial integrity.
How do Accounting Systems utilize a Chart of Accounts?
Accounting serves as a fundamental framework for organizations to systematically record and analyze financial transactions. A well-structured Chart of Accounts is integral to this process, as it categorizes financial data according to basic accounting methods. This organization requires the establishment of various accounts, which facilitate the tracking of income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. Consequently, these accounts provide information that is crucial for assessing an entity’s financial performance.
For instance, a Chart of Accounts may include accounts such as Cash, Accounts Receivable, Inventory, Accounts Payable, and Equity. Each of these accounts plays a vital role in ensuring that financial reporting is accurate and comprehensive. By utilizing a Chart of Accounts, organizations can effectively manage their financial data and make informed decisions based on reliable information.
How do Accounting Systems incorporate the General Ledger?
Accounting systems fundamentally incorporate the General Ledger as a central component essential for accurate financial reporting. The two basic accounting methods, namely cash and accrual accounting, require meticulous tracking of all financial transactions. This is where the General Ledger plays a pivotal role, serving as the primary record of all accounts. Furthermore, effective accounting requires the integration of various modules, including accounts payable, accounts receivable, payroll, inventory, and fixed assets, ensuring comprehensive financial management.
By systematically categorizing financial data, the General Ledger facilitates the generation of financial statements, which are crucial for stakeholders. Additionally, the General Ledger supports auditing processes by providing a clear trail of transactions. This integration not only enhances the accuracy of financial reporting but also bolsters the overall efficiency of the accounting system.
How do Accounting Systems integrate modules like Accounts Payable and Receivable?
Accounting systems effectively integrate modules such as Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable to streamline financial operations. This integration facilitates real-time data sharing, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. For instance, automated invoice processing reduces manual entry errors, while synchronized reporting allows for comprehensive financial analysis. Furthermore, the ability to track payment statuses improves cash flow management, and integrated budgeting tools enable better financial forecasting. Overall, these systems foster a cohesive financial environment that supports informed decision-making and operational excellence.
How do Accounting Systems facilitate financial reporting?
Accounting systems play a pivotal role in facilitating financial reporting by ensuring accuracy, consistency, and efficiency in data management. For instance, they provide automated data entry to minimize human error, while real-time data processing allows for timely updates of financial information. Additionally, these systems often include integrated reporting tools that streamline the generation of financial statements. Furthermore, they enhance compliance tracking with regulatory standards, and offer data analytics capabilities to support informed decision-making.
How Do Various Types of Accounting Systems Operate and Differ?
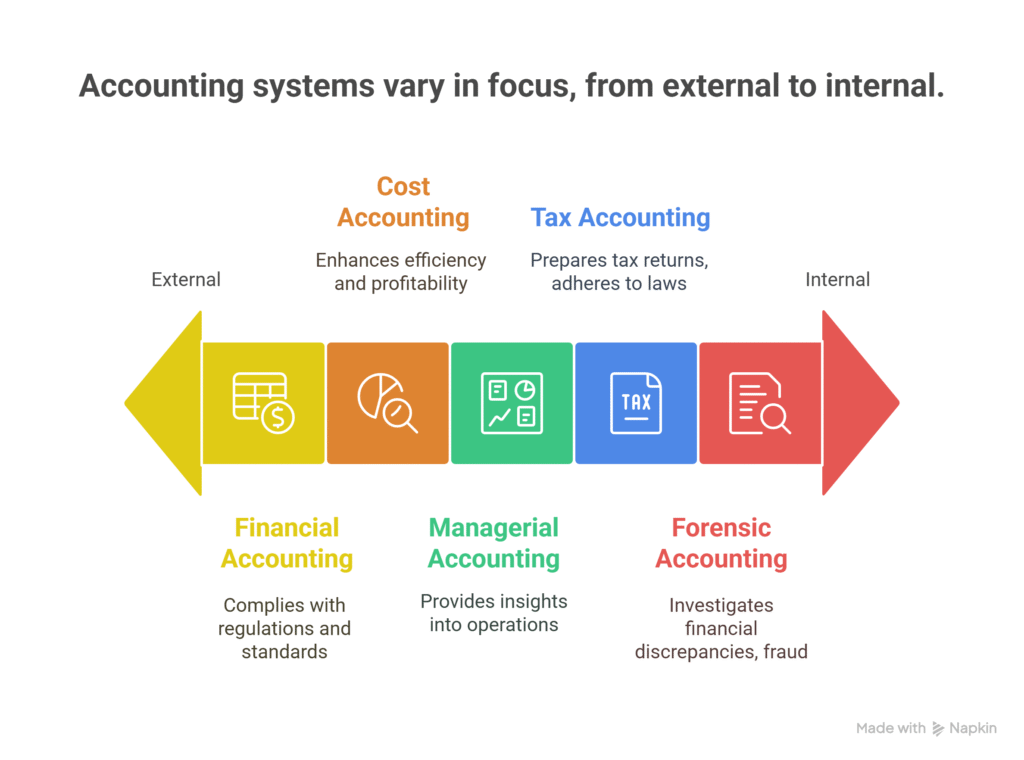
Various types of accounting systems operate under distinct methodologies, each tailored to meet specific organizational needs. For instance, financial accounting focuses on the systematic recording and reporting of financial transactions, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. In contrast, managerial accounting emphasizes internal decision-making by providing detailed insights into operational performance. Another example is cost accounting, which analyzes production costs to enhance efficiency and profitability. Additionally, tax accounting is specialized in preparing tax returns and ensuring adherence to tax laws, while forensic accounting investigates financial discrepancies and fraud. Each system serves a unique purpose, reflecting the diverse requirements of businesses.
How did manual Accounting Systems traditionally function?
Traditional manual accounting systems functioned through a series of systematic processes that required meticulous attention to detail. Journals were utilized to record transactions chronologically, while ledgers served as the primary tool for categorizing these entries. Additionally, trial balances were prepared to ensure that debits equal credits, providing a preliminary check on accuracy. The preparation of financial statements followed, summarizing the company’s financial position. Finally, reconciliation processes were conducted to verify that records matched bank statements and other financial documents.
What capabilities do computerized Accounting Systems offer over manual methods?
Computerized Accounting Systems offer a range of capabilities that significantly surpass manual methods. Firstly, they provide increased accuracy by minimizing human errors through automated calculations. Secondly, these systems facilitate real-time reporting, allowing for immediate access to financial data and insights. Thirdly, they enhance data security through encryption and user access controls, safeguarding sensitive information. Fourthly, computerized systems enable scalability, easily accommodating the growth of a business without extensive reconfiguration. Lastly, they support integrated functionalities, allowing seamless interaction with other business applications, thus streamlining overall operations.
How do on-premise versus cloud-based Accounting Systems compare for modern needs?
In the contemporary business environment, the comparison between on-premise and cloud-based accounting systems reveals distinct advantages and challenges. Firstly, scalability is a significant factor, as cloud solutions typically offer greater flexibility to accommodate growth. Secondly, cost-effectiveness is often more pronounced in cloud systems, reducing the need for substantial upfront investments. Thirdly, accessibility is enhanced through cloud platforms, allowing users to manage finances remotely. Additionally, security measures can vary, with cloud providers often implementing advanced protocols. Lastly, integration capabilities may be superior in cloud systems, facilitating seamless connections with other software applications.
When are Enterprise Resource Planning systems considered as comprehensive Accounting Systems?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are regarded as comprehensive Accounting Systems when they integrate various financial functionalities, thereby enhancing organizational efficiency. For instance, an ERP can manage accounts payable, accounts receivable, general ledger, financial reporting, and budgeting processes seamlessly. This integration allows for real-time data analysis and improved decision-making capabilities. Furthermore, such systems facilitate compliance with regulatory standards, ensuring that all financial transactions are accurately recorded and reported. Consequently, the holistic nature of ERP systems positions them as invaluable tools for modern businesses.
How Can the Right Accounting System Be Effectively Chosen?
Choosing the appropriate accounting system requires careful consideration of various factors that align with the specific needs of a business. Firstly, it is essential to evaluate the scalability of the system; a solution that accommodates growth will ensure long-term viability. Secondly, the user-friendliness of the interface can significantly impact the efficiency of the accounting process. Thirdly, integration capabilities with other software, such as CRM or inventory management systems, must be assessed to enhance operational synergy. Additionally, the cost-effectiveness of the system should be analysed, ensuring it fits within the budgetary constraints while providing necessary features. Lastly, seeking customer support options is crucial, as ongoing assistance can facilitate smoother transitions and troubleshooting.
What business factors should an Accounting System align with during selection?
When selecting an accounting system, it is imperative that the system aligns with several critical business factors. First, the system should accommodate scalability to support future growth and increased transaction volumes. Additionally, it must ensure regulatory compliance with applicable financial laws and standards. Furthermore, the chosen system should facilitate integration with existing software and processes to promote operational efficiency. Another essential factor is the user-friendliness of the interface, which impacts employee training and productivity. Lastly, the system should provide robust reporting capabilities to support informed decision-making.
How should an Accounting System meet budget and scalability needs?
An effective accounting system must adeptly address both budgetary constraints and scalability requirements. To achieve this, it should incorporate cost-effective solutions that minimise overhead while maximising efficiency. Furthermore, the system should offer flexible reporting tools that allow for real-time financial analysis, enabling organisations to make informed decisions. Additionally, the system needs to support multi-currency transactions to facilitate international operations. Integration with existing software and cloud-based storage options can enhance accessibility and ensure seamless growth. Lastly, the system must provide user-friendly interfaces to accommodate varying levels of expertise among staff members.
What features and integrations should an Accounting System provide for optimal performance?
To achieve optimal performance, an accounting system should incorporate several essential features and integrations. Firstly, it must provide real-time financial reporting to facilitate informed decision-making. Secondly, seamless bank reconciliation capabilities are crucial for maintaining accurate financial records. Thirdly, the system should support multi-currency transactions to cater to global business operations. Additionally, robust tax compliance tools are necessary to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements. Lastly, integration with payroll systems enhances operational efficiency by streamlining employee compensation processes.
How Are Accounting Systems Typically Implemented and Used Day-to-Day?
Accounting systems are typically implemented through a structured process that includes several key phases. Initially, organisations assess their specific needs and select an appropriate software solution, such as QuickBooks, Sage, or Oracle NetSuite. Following software selection, data migration and system configuration are conducted to ensure that existing financial information is accurately transferred. Training sessions are essential for staff to effectively utilise the system on a day-to-day basis. Subsequently, daily operations involve tasks such as transaction recording, financial reporting, and budget tracking, which facilitate informed decision-making and enhance overall financial management.
What initial setup steps do Accounting Systems require?
Setting up an accounting system requires several critical initial steps to ensure its effectiveness and accuracy. Firstly, it is essential to define a chart of accounts, which categorises all financial transactions. Secondly, one must establish user roles and permissions to ensure data security and appropriate access levels. Thirdly, configuring financial reporting templates is vital for generating insightful reports. Additionally, integrating bank feeds can streamline transaction processing. Lastly, it is important to customise tax settings to comply with local regulations.
How do Accounting Systems record and process daily transactions?
Accounting systems meticulously record and process daily transactions through a structured methodology that ensures accuracy and compliance. Initially, transactions are captured using source documents such as invoices, receipts, and bank statements. Subsequently, these entries are classified into appropriate accounts, facilitating the organisation of financial data. The system then summarises the information, producing reports that reflect the company’s financial status. Finally, the data is analysed to support strategic decision-making and enhance financial performance.
How can Accounting Systems be leveraged for ongoing financial analysis?
Accounting systems serve as vital tools for ongoing financial analysis, enhancing decision-making processes within organisations. Real-time reporting capabilities allow for immediate insights into financial performance, facilitating timely interventions. Additionally, budget variance analysis enables businesses to compare actual results against forecasts, identifying discrepancies and areas for improvement. Furthermore, the integration of predictive analytics can aid in forecasting future financial trends based on historical data. Lastly, cash flow management tools within these systems help maintain liquidity, ensuring that organisations can meet their financial obligations effectively.
What Advanced Considerations Influence the Long-Term Success of Accounting Systems?
In the realm of accounting systems, several advanced considerations critically influence their long-term success. Firstly, the integration of cloud technology allows for real-time data access and enhances collaboration among stakeholders. Secondly, the implementation of automated processes significantly reduces human error and increases efficiency. Thirdly, the adaptability of the system to comply with evolving regulatory standards ensures ongoing relevance and reliability. Furthermore, the incorporation of data analytics facilitates informed decision-making by providing actionable insights. Lastly, the emphasis on user training promotes effective utilization of the system, ultimately contributing to its sustained effectiveness and success.
What common pitfalls should be avoided when managing Accounting Systems?
When managing accounting systems, it is imperative to avoid several common pitfalls that can compromise financial integrity. Firstly, neglecting regular updates can lead to outdated software, increasing vulnerability to errors. Secondly, insufficient user training may result in improper data entry, undermining the accuracy of financial reports. Thirdly, failing to implement internal controls can expose the organisation to fraud and mismanagement. Additionally, overlooking data backup procedures may jeopardise critical financial information. Lastly, ignoring regulatory compliance can result in legal repercussions and financial penalties.
How can data security risks be mitigated with respect to Accounting Systems?
To effectively mitigate data security risks associated with Accounting Systems, organizations can implement several strategic measures. Firstly, employing robust encryption protocols ensures that sensitive financial data remains protected during transmission and storage. Secondly, regular software updates and patches can address vulnerabilities that may be exploited by cybercriminals. Thirdly, adopting a comprehensive access control policy limits data exposure to authorized personnel only. Additionally, conducting frequent security audits can identify and rectify potential weaknesses in the system. Lastly, providing employee training on cybersecurity best practices fosters a culture of vigilance against threats.
Why is inadequate training a challenge for users of Accounting Systems?
Inadequate training presents a significant challenge for users of accounting systems, as it leads to a myriad of operational inefficiencies. Firstly, users may struggle with data entry, resulting in inaccuracies that can skew financial reports. Secondly, the inability to navigate the system effectively can hinder report generation, causing delays in decision-making. Thirdly, insufficient training may prevent users from utilizing automation features, which are essential for streamlining processes. Additionally, a lack of understanding can impair compliance management, exposing the organization to legal risks. Lastly, inadequate training can diminish user confidence, ultimately affecting system adoption and overall productivity.
When Should a Business Re-evaluate or Upgrade its Existing Accounting Systems?
Businesses should consider re-evaluating or upgrading their existing accounting systems under several circumstances. For instance, when experiencing significant growth, the current system may become inadequate to handle increased transaction volumes. Additionally, if the organization undergoes a merger or acquisition, a more robust system might be necessary to integrate financial data effectively. Furthermore, the emergence of new regulatory requirements can necessitate an upgrade to ensure compliance. Another critical moment is when the existing system frequently encounters errors or inefficiencies, which can hinder operational effectiveness. Lastly, adopting advanced technology can enhance analytical capabilities and improve decision-making processes.
What signs indicate the need for more advanced Accounting Systems?
Organisations may recognise the necessity for more advanced accounting systems through several key indicators. Firstly, an increase in transaction volume can signal that current systems are becoming overwhelmed, necessitating a more robust solution. Secondly, the emergence of complex regulatory requirements may require enhanced compliance features. Thirdly, a lack of real-time financial reporting can hinder decision-making processes. Additionally, the need for improved data security is paramount as businesses grow. Lastly, the desire for advanced analytical capabilities can drive the transition to a more sophisticated accounting system.
How does technological evolution impact the lifecycle of Accounting Systems?
The technological evolution significantly influences the lifecycle of Accounting Systems by introducing enhanced functionalities and efficiencies. For instance, the integration of cloud computing allows for real-time data access, thereby improving collaboration and decision-making. Additionally, the adoption of artificial intelligence facilitates automated data entry and analysis, reducing human error. Furthermore, the implementation of blockchain technology ensures greater transparency and security in financial transactions. Lastly, the emergence of mobile applications empowers users to manage their accounts remotely, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness.
